93% Cu Recovery in a Stirred Tank Bioleach Amenability Tests Performed on Haib Copper Mineralized Material from Namibia
(TheNewswire)




Vancouver, B.C., Canada - TheNewswire – August 28, 2019 – Deep-South Resources Inc. ("Deep-South" or “the Company") (TSXV:DSM) announces results from microbial-assisted stirred tank leach amenability tests performed on stockpile material from the Haib Copper Project in Namibia. The test work program is managed by METS Engineering of Australia and undertaken by Mintek in South Africa.
Bioleach test work results summary:
Two tons of feed material was collected for the test work. The samples were removed from a stockpile extracted from an adit dug in the higher grade area of the main Haib deposit. The samples have not been weathered and are considered representative of the sulphide mineralized material at Haib.
The tests were performed on fine-milled material as a pre-cursor to column leach test work in order to indicate the maximum copper dissolution that can be achieved at 65oC in the absence of liberation restraints (as would be present in coarse rocks).
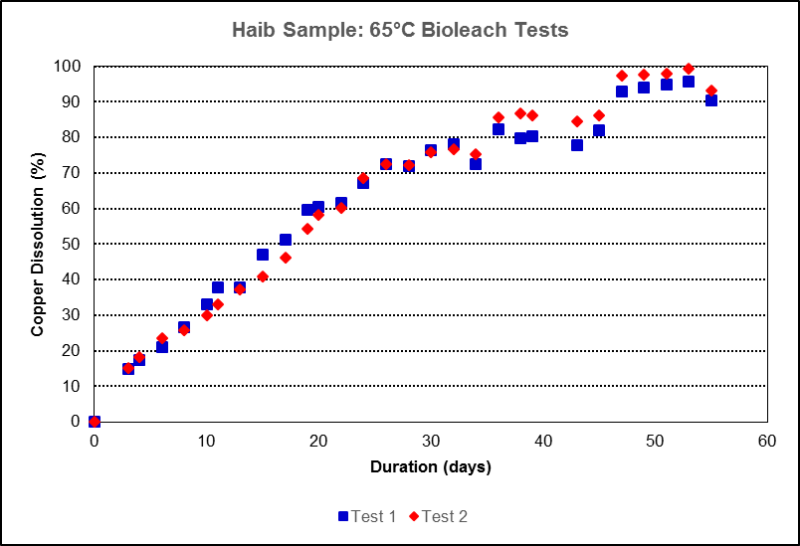
Duplicate batch bioleach amenability tests were performed on fine-milled (P80 of 75 µm) mineralized ore in 2 L agitated tanks. Copper dissolutions of 90.5% and 93.1% were obtained after 54 days, corresponding to recalculated copper head grades of 0.69% and 0.71%, respectively. Copper dissolution profiles are presented in
Figure 1. Stirred tank copper dissolution profiles
Six - 1 metre columns have been initiated at Mintek on -4.7mm, -3.35mm and -2.36mm mineralized material and the copper leaching recovery is progressing ahead of plan. It is important to note that the expected leaching time period in columns will be longer than in stirred tanks.
Mr John Akwenye, Chairman of Deep-South stated that: “the bio-assisted leaching results combined with grade upgrading ore sorting results, HPGR and agglomeration are highly promising and demonstrate that we are on the right path to extract the metal at Haib at low costs and low capital expenditures.”
There are no deleterious elements. The mineralogy of the milled Haib feed revealed that 98.5% of the total copper content occurred as chalcopyrite, 1% as bornite, and less than 0.5% as chalcocite, covellite, malachite and chrysocolla.
High Pressure Grinding Roll (HPGR) optimisation tests demonstrated that the hard Haib mineralized material is amenable to HPGR. A pressure of 60 bar is deemed suitable as the particle size distribution was not reduced once the pressure exceeded this value.
The mineralized material agglomerated without any issues. Heap leaching relies on the ability of the leaching solution to penetrate through the mound, around the mineralized material particles. When the mineralized material is not agglomerated, fine particles may vary in size and shape, reducing the ability of the solution to percolate efficiently through the heap, as smaller fines clog the spaces between larger fines. An agglomeration drum was used to agglomerate the mineralized material and increase uniformity, making it easier for the leaching solution to percolate through the channels between particles to help maximize copper dissolution.
Further results will be disclosed during the course of the test work scheduled to continue until December 2019.
Qualified Person
Damian E.G. Connelly, BSc (Applied Science), FAusIMM, CP (Met), Director of Mineral Engineering Technical Services is responsible for the technical part of this press release and is the designated Qualified Person under the terms of National Instrument 43-101.
About Mintek:
Mintek is South Africa’s national mineral research organisation established in 1934 to assist in ensuring sustainable growth in the minerals and metal industries through research, development & innovation (RDI).
The organisation has grown over the years into an internationally competitive, respected research and development centre of metallurgical and mineral processing technologies. Mintek’s Biotechnology Division has been involved in the development of tank and heap bioleaching technologies for over 30 years. Mintek also specialises in hydrometallurgy, including leaching, precipitation, solvent extraction and electrowinning. You can visit Mintek at : https://www.mintek.co.za
About METS :
Established in 1988, Mineral Engineering Technical Services provides a range of services in the fields of Minerals Processing, Hydrometallurgy and Pyrometallurgy. METS is the engineering company that produced Deep-South’s Preliminary Economic Assessment (PEA) disclosed on February 26, 2018. You can visit METS at : https://www.metsengineering.com
About Deep-South Resources Inc.
Deep-South Resources Inc. is a mineral exploration company largely held by Namibian shareholders and Management with 25% and Teck Resources Ltd with 28% of Deep-South share capital. Deep-South currently holds 100% of the Haib Copper project in Namibia, one of the largest copper porphyry deposits in Africa. Deep-South’s growth strategy is to focus on the exploration and development of quality assets, in significant mineralized zones, close to infrastructure, in stable countries.
This press release contains certain "forward-looking statements," as identified in Deep- South’s periodic filings with Canadian Securities Regulators that involve a number of risks and uncertainties. There can be no assurance that such statements will prove to be accurate and actual results and future events could differ materially from those anticipated in such statements.Neither the TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in the policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this release.
More information is available by contacting Pierre Léveillé, President & CEO at
+1-819-340-0140 or at: info@deepsouthresources.com or Paradox Public Relations at +1-514-341-0408.
Copyright (c) 2019 TheNewswire - All rights reserved.