Medallion Launches New Clean Energy Technology Strategy
Builds on Medallion’s Existing Rare Earth Processing Technologies
Comprehensive Plan Proposed to Shareholders
NOT FOR DISTRIBUTION TO U.S. NEWSWIRE SERVICES OR DISSEMINATION IN THE U.S.
VANCOUVER, British Columbia, April 26, 2022 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Medallion Resources Ltd. (TSX-V: MDL; OTCQB: MLLOF; Frankfurt: MRDN – “Medallion” or the “Company”), is pleased to announce the launch of a new strategic plan (the “Strategic Plan”) to position the Company in the near term as a technology leader within the industries essential to the generation, storage, and efficient use of clean energy. Key parts of the plan include a strengthened executive leadership team, up-listing to Nasdaq Capital Markets, and rebranding as Medallion Innovations Corp. to better reflect the future direction of the Company.
Medallion’s focus has been to identify and develop innovative technologies for the rare earth element (“REE”) industry that, when compared with incumbent technologies, are lower cost and reduce the environmental and social impacts of production.
Implementation of the new Strategic Plan is intended to enhance Medallion’s existing REE processing technology portfolio by identifying, incubating and gaining exclusive rights to the commercialization of additional innovative technology platforms across the entire REE value chain and broadening its focus to include other high-performance materials. Medallion believes that its technology portfolio will continue to facilitate the production of materials, deployment of processes, and/or generation of essential data for the clean energy transition.
The clean energy transition, involving the widespread generation of renewable energy and the electrification of transport is now demonstrating dramatic growth that is at risk because of weaknesses in global supply chains. Medallion’s new Strategic Plan reflects the global shift from fossil fuel-based to a minerals-based economy centered on “friendly nations” and is intended to position the Company for better access to capital, a larger playing field, and importantly the ability to build a team with the essential skills and experience in technology development and commercialization.
Medallion believes that up-listing to the Nasdaq Capital Markets (“NasdaqCM”) will significantly strengthen the Company’s profile and increase the capacity for US and international shareholders to invest in the REE and clean energy technology sectors.
Upon completion of the Nasdaq up-listing, Alfredo Ramos Plasencia will join the Company as Chief Executive Officer and Director, while Dr. Kurt Forrester will join the management team as Chief Technology Officer and continue to serve as a Director. Mark Saxon will continue as a Director and assume a business development role focused on mining industry opportunities.
As previously announced, the Company has engaged Chardan Capital Markets LLC (“Chardan”) to advise on an up-listing and simultaneous financing. The up-listing to the NasdaqCM is conditional on Nasdaq accepting the Company’s listing application, including the Company’s plan to meet the Initial Listing Requirements, and a registration statement being declared effective by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”). The Company is preparing to file a registration statement with the SEC on Form F-1 before the Annual General and Special Meeting of Shareholders (the “Shareholders’ Meeting”) on May 27, 2022 in Vancouver, B.C.
Medallion has begun the Nasdaq listing application process and has reserved the trading symbol “MDL” for trading on NasdaqCM after the up-list.
Medallion President & CEO Mr. Saxon stated “Medallion is setting the course for a strong and positive impact in the supply of materials and technologies for the energy transition. Our recent successful partnerships in the REE sector, based on deep industry knowledge and connections, have laid the groundwork for where we see many value-add opportunities. The proposed business and management changes deliver the opportunity to accelerate in line with the renewable energy and EV markets.”
Mr. Ramos stated, “I am excited to be entrusted with the CEO role at Medallion at this key time in the Company’s history. My experience in the identification, incubation and commercialization of breakthrough technologies matches well with the new Strategic Plan. Medallion’s past investment in REEs and methodology in identifying new investment opportunities provides an excellent platform for future development.”
Medallion – the New Vision
The clean energy transition has triggered a fundamental change in the consumption of materials, as single-use oil, gas and coal is replaced by renewable energy alternatives. Energy generation and storage is now increasingly linked to high performance, critical raw materials at a time of heightened supply chain vulnerability, which has been exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic and recent geopolitical instability. Over the past decade, the U.S., Europe, Japan, and Korea have increasingly focused on the supply chain for critical minerals and, in the U.S., REE supply chain resilience is a bipartisan issue.
Medallion believes that meeting demand for critical raw materials for the energy transition will require investment in more efficient and effective processing technologies, with reduced energy footprints. The extraction of critical raw materials as byproducts of other activities, and increased recycling of critical minerals from end-of-life products, provide immediate and attractive opportunities without the need for additional mining.
Medallion believes it is essential that minerals required for the clean energy transition be produced in accordance with ESG best practices. The production of EVs and clean energy technologies should not cause harm to the communities or the environment where they are produced.
The new Strategic Plan that the Company will seek to implement upon completion of the up-listing to NasdaqCM and associated financing includes:
- Strengthened executive management team
- CEO: Alfredo Ramos Plasencia
With more than 20 years’ experience in the process industries, Alfredo has worked in diverse research and development, engineering and operational roles across a wide range of sectors including chemicals, energy and mining. Alfredo has key expertise in digital design and smart manufacturing solutions having developed and commercialized novel technologies supporting design, engineering and operation of industrial production assets. He holds a Masters in chemical engineering from RWTH Aachen University (Dipl.-Ing.) and an MBA, with distinction, from London Business School. - CTO: Kurt Forrester
During his 16-year career Kurt has been professionally engaged as an engineering consultant in the metals and minerals, environmental and applied research domains. This has included process and technology development, feasibility assessment (PEA, PFS, BFS) as well as detailed design (EPCM). He has broad experience across commodities and technologies including in base metals, rare earth elements and industrial minerals. A graduate of the University of Sydney (2001) with a BEng (Hon 1st) in Chemical Engineering and more recently with a PhD in Engineering (2007) he is also a Chartered Chemical Engineer and Chartered Professional Metallurgist. - Mark Saxon will continue to serve as a Director and strategic advisor.
- CEO: Alfredo Ramos Plasencia
- Rare earth elements: Medallion plans to continue to invest in the development of the existing REE-focused technology portfolio. Furthermore, the Company proposes to continue the evaluation and seek to secure complementary REE technologies to provide a full suite of processes from raw material inputs to metals and alloys.
- Other clean energy technologies: Medallion is identifying market needs, will assess alternative technologies, and ultimately support commercial development of innovative, disruptive intellectual property related to clean energy with clear paths to commercialization.
Implementation of the up-listing will require the Board to take certain actions in order to comply with the Initial Listing Requirements under Nasdaq Rules 5505(a) and 5505(b)(1) including consolidation of the Company’s shares in order to meet the minimum bid price of US$4.00 per share. Based on the recent trading price of approximately US$0.09 per share, meeting the minimum bid price would require a consolidation of at least 1-for-45.
At the Shareholders’ Meeting, shareholders are being asked to approve de-listing the Company’s shares from the TSX Venture Exchange upon approval by Nasdaq of trading the Company’s shares on NasdaqCM.
Initial Focus on Rare Earth Elements
Under the new Strategic Plan, Medallion’s initial focus is to continue commercialization of its two REE processing technologies: the Medallion Monazite Process (MMP) developed by the Company, and the Ligand Assisted Displacement (LAD) Chromatography REE separation process initially developed by Purdue University and licensed from Purdue Research Foundation (“Purdue”). Medallion is continuing to evaluate other REE-related technologies including metallization and magnet recycling.
REE permanent magnets are critical components of motors in electric vehicles, generators in wind turbines and are an essential part of the modern economy, performing core functions in components of trillions of dollars in global GDP including clean energy, transportation, consumer electronics, medical equipment, robotics, and national defense.
Medallion developed the MMP to address health, safety, environmental and economic challenges associated with established processing technology. The Company identified the need for better technology solutions, undertook internal research and process engineering, and developed MMP to be ready for scale-up to demonstration plant and then commercial scale operations.
MMP extracts mixed REE concentrate from mineral sand monazite, which is accumulated as a byproduct from heavy mineral sand mining. The MMP adds value to a material that is already mined, such that there is no incremental mining activity.
Medallion also identified the need to separate salable REE compounds from mixed concentrates using less energy and fewer reagents than current standard practice. The Company completed extensive technical evaluation of alternative technologies and identified the LAD Chromatography process as a potential market-leading opportunity. Medallion entered into an agreement with Purdue whereby the Company and Purdue are jointly advancing the LAD process to separate REEs from all raw material feed stocks excluding coal sources and recycled materials.
Medallion anticipates the LAD Chromatography process can reduce capital and operating costs for REE separation compared with incumbent technologies, and be readily adaptable to multiple feedstocks, including but not limited to monazite.
On March 28, 2022, following a technology review, Medallion announced it had secured exclusive rights to evaluate a proprietary and privately-owned metallization process, where REE compounds are converted to REE metal, a crucial step in the production of high strength REE permanent magnets. There are few entities outside China that have this metallization capacity. The novel and innovative technology would enable conversion of REE compounds to metal in a continuous process, requiring less energy than incumbent processes and without toxic fluorine chemistry.
If the evaluation is positive, Medallion will seek to secure exclusive rights to the technology at which point the Company would have a full suite of REE processing technologies from concentrate to feedstock for magnet manufacturing.
Future Opportunities
As part of the new Strategic Plan, Medallion is building the team and capital structure to enable replication of the evaluation and commercialization approach that identified and delivered access to the LAD Chromatography process. This approach also led to the recent identification of the REE metallization and recycling technologies and includes evaluation of commercial needs, assessment of alternative technologies, identification of undervalued disruptive technology, and support commercial development of additional intellectual property (IP) with clear paths to commercialization.
Rare Earth Industry Overview and Market Opportunity
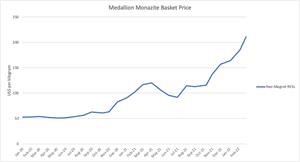
Commercially, the most important use of REEs is in high strength permanent magnets. Neodymium-iron-boron (“NdFeB” or “neo”) permanent magnets use a combination of neodymium (“Nd”) and praseodymium (“Pr”) with additional dysprosium (“Dy”) and terbium (“Tb”) when required for high-temperature application. These four elements, collectively the neo magnet rare earth elements, represent more than 90% of the value of REEs in mineral sand monazite feedstock evaluated by Medallion for processing by MMP to produce cerium depleted mixed oxides. The basket price of these neo magnet REOs, based on REO prices reported by Asian Metals, has doubled since 2020 to approximately $200/kg but remains at less than half the mid-2011 peak of $443/kg.
Figure 1: Basket Price of Neo Magnet REOs contained in monazite feedstock
https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/7f6edac8-b6d3-456c-bf29-c585c69db04f
The U.S. Geological Survey’s (“USGS”) report “Mineral Commodity Summaries 2022” estimates that China mined approximately 60% of the world’s REEs in 2021, followed by the U.S. (15%), Myanmar (9%), Australia (8%) with the rest of the world contributing approximately 8%. Of particular note, in 2021 all the production from the U.S. and Myanmar, and some of the Australian REE production was processed in China, such that downstream value was created within China. The USGS reported the U.S. as being 100% dependent on imported REEs for downstream manufacturing.
REEs are extracted from three major geological sources: monazite, bastnasite, and ionic clays. Prior to the mid-1960s, most of the world’s production of REEs was from monazite sourced from mineral sands.
The REE industry was transformed by the discovery in 1949 of the Mountain Pass bastnasite deposit in southern California.
China started to produce significant amounts of REEs in the 1980s and rapidly came to dominate mining and processing, including downstream manufacturing of rare earth magnets.
Supply Chain Vulnerability
Under the “Made in China 2025” initiative, China is moving downstream in the production cycle, aiming to produce more manufactured and semi-manufactured goods for domestic consumption or export in contrast to its previous focus on exporting low value raw materials.
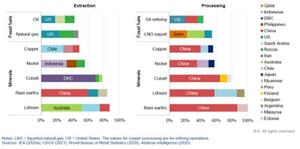
Figure 2: Share of top three producing countries in global production of selected minerals and fossil fuels – The Role of Critical Minerals in Clean Energy Transitions, IEA, Paris https://www.iea.org/reports/the-role-of-critical-minerals-in-clean-energy-transitions.
https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/aff8d4e2-7e0f-48b3-a045-29f69bcb3bd5
Despite the importance of REEs to modern industry, the REE supply chain demonstrates a high degree of vulnerability. Currently, mineral concentrates from Mountain Pass are shipped from the California to China for processing and concentrates from Mount Weld are shipped from Australia to Malaysia, and some of the mixed oxides produced in Malaysia are then shipped to China for further processing.
Disrupting the REE supply chain has been a tool in past international conflicts. Following a territorial dispute in 2010 between China and Japan regarding the Senkaku Islands, China restricted supplies of REEs to Japan which caused market prices to surge ten-fold or more between early 2010 and late 2011.
U.S. Government policies support both domestic production and production within the National Technology and Industrial Base (“NTIB”) countries – namely the U.S., Australia, Canada, and the United Kingdom – and other “friendly” nations.
President Biden has indicated a preference for upstream mining and initial processing in Australia and Canada with downstream manufacturing in the U.S.
Key markets driving medium- and long-term demand for REEs
Medallion expects the major drivers of demand for REEs to be permanent magnets used in electric vehicles, wind turbines and other high growth markets.
Electric Vehicles (EV)
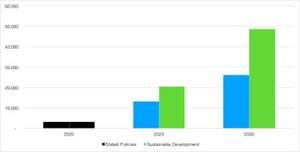
The accelerating transition from internal combustion engines (ICE) to EVs is well documented. The International Energy Agency’s (IEA) Global EV Data Explorer (https://www.iea.org/articles/global-ev-data-explorer) assesses global EV sales under its sustainable development scenario (SDS) needed to meet the targets set by the 2015 Paris Climate Accords and a more conservative forecast based on stated policies (STEPS) that have already been announced.
The IEA projects that global EV sales in 2030 will be between 26 million and 49 million units, or between 8 and 15 times the sales of 3.2 million units in 2020, with growth of sales of trucks and buses expected to outpace the growth in the sales of cars and light trucks. The IEA projections equate to between 23% and 31% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for cars and light trucks and between 26% and 39% for trucks and buses from 2020 to 2030.
Figure 3: International Energy Agency's (IEA) Projections of Global EV sales
https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/8cf7d781-2fed-416d-8ca5-4820d6379f54
There are two types of electric motors in EVs: induction and permanent magnet motors. Permanent magnet motors are generally recognized as offering greater range and performance – Tesla adopted permanent magnets for the Model 3 and subsequently for the smaller front motors in its older models.
Medallion estimates that EV’s represent approximately 10% of global demand for neo magnets in 2019/2020. If the EV market grows ten-fold by 2030 it would consume all the current production of neodymium and praseodymium (“NdPr”).
Due to high temperature operating conditions, neo magnets in EVs require dysprosium and terbium (“DyTb”) in the alloy to prevent demagnetization. Medallion estimates that neo magnets in EVs represent a larger share of the DyTb market than of the NdPr market and therefore anticipates that the effect of EVs will be greater.
Wind Turbines
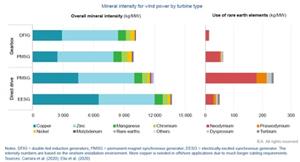
Wind turbine technology has evolved rapidly to include variable speed turbines which can either power an induction generator via a gearbox or a permanent magnet generator using a direct drive system. By eliminating the gearbox, direct-drive wind turbines are more reliable and easier to maintain as well as lighter and capable of generating electricity at lower wind speeds. Weight and reliability are most important for the largest, offshore wind turbines that are being manufactured today.
Figure 4: Mineral Intensity for wind power by turbine type, International Energy Agency
https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/9a8567f7-0473-4435-8436-0c03edefbc6e
Medallion’s Technologies
Medallion currently has two REE process technologies, namely the Medallion Monazite Process (MMP) and the Ligand Assisted Displacement (LAD) Chromatography Process, and is in the advance stages of evaluating a third REE process technology for metallization and recycling. Additionally, the Company continues to seek to identify and acquire process technologies or methods to complement and/or extend our current portfolio and enable the clean energy transition.
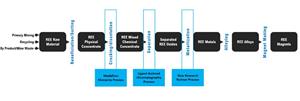
Figure 5: Industry Position of Medallion Technology Platforms
https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/30a271fa-07e4-4e10-af0d-480ec42b3a92
Medallion Monazite Process
The proprietary MMP focusses on recovering mixed REE concentrates from monazite, a byproduct of many heavy mineral sand operations that produce the bulk of the world’s supply of titanium and zirconium. The Company designed the MMP to be highly automated, safe and cost efficient. The MMP is not limited to processing byproduct monazite and could be deployed on hard-rock derived monazite from primary mining operations.
There are several important criteria for successful extraction of REEs from monazite. Cerium, the most abundant REE (typically making up 40% of the total REE content of monazite), is mainly used in relatively mature markets such as catalysts, pigments and phosphors. As demand for NdPr for neo magnets has driven increased production of all REEs, cerium has move to oversupply. The value of the cerium in a typical monazite concentrate is less than the additional separation and transportation cost. MMP incorporates a low-cost method to remove cerium. Monazite typically contains actinides (uranium and thorium), which must be removed from the REE circuits. In the past, these actinides have not always been handled with appropriate concern for health, safety and the environment. The MMP allows the removal of these elements in a safe and stable form.
In 2012, Medallion commissioned a report by SENES Consultants Limited to review the health and safety aspects of Medallion’s proposed monazite processing. SENES supported the Company’s view that a highly automated commercial scale monazite processing plant can be operated safely in compliance with international mineral processing health, safety, and environmental standards.
With this confirmation of concept, Medallion sought to develop a better process that builds on the commercially standard practice – a two-step process of caustic monazite digestion and acid leaching of the caustic residue – with the following design objectives:
- Scalable, to ensure deployments can accommodate growth
- Transferable, to ensure the Process can be deployed on multiple feedstock sources and/or multiple geographic locations
- Extensible, to ensure the Process can be customized and augmented based on constraints imposed by the locality of the deployment
- Efficient, minimizing the demand on energy and consumables while maximizing the utilization and valorization of metals contained in the monazite
- Automated, to reduce operator exposure to a challenging work environment as well as operate an economically-lean workforce with enhanced safety
- Modular, in support of both the scalable and extensible design objectives a modular approach has been adopted to expansion and customization of the Process
Initial process development began with laboratory-scale success using the caustic metallurgical process. During subsequent development work, the Company produced a mixed REE carbonate concentrate provided to a third-party for initial product qualification that confirmed the suitability of the material for that party’s process.
In 2018 the Company completed bench-scale production of cerium-depleted REE concentrate. This early version of the MMP process incorporated the removal of cerium, significantly increasing the value per kilogram of the REE concentrate. This phase of test work produced a mixed REE carbonate concentrate which would satisfy the quality specifications of established REE refineries.
The Company completed development of the proprietary flowsheet for the MMP process in 2019. Key features of the process enable:
- High degree of process automation for enhanced safety by isolating workers from harsh operating environments
- Highly-energy efficient design employing energy recovery systems
- Option for a zero-liquid discharge plant to provide additional flexibility on planning/permitting
- Waste production options, and
- “Off-the-shelf” equipment – the innovations relate to how the equipment is configured and used.
In November 2019, Medallion engaged Australian-based Simulus Engineers, an independent engineering consultancy, to develop a chemical process model for the MMP process. The integrated process model incorporated the findings from the test work programs and confirmed the technical viability of the complete process.
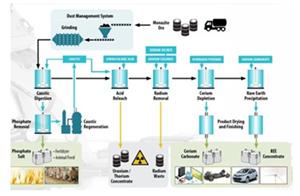
MMP Process Flowsheet
The MMP process is designed to produce high-purity mixed REE as a chemical concentrate as well as byproduct trisodium phosphate (“TSP”), and radioactive materials in a form where they can be handled effectively for market or storage. In November 2020 Medallion extended Simulus Engineers’ engagement to include a confidential techno-economic assessment (“TEA”) of the MMP process.
The TEA evaluated a commercial-scale facility processing 7,000 metric tons per year of monazite feedstock. Simulus estimated the capital cost at $34 million including 15% contingency and annual operating costs of approximately $21 million, excluding the cost of the monazite feedstock.
Figure 6: Simplified schematic representation of the Medallion Monazite Process flowsheet
https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/870cb2bc-1a2c-40ea-be66-a736e79d458c
The TEA estimated the facility would produce approximately 870,000 kilograms of NdPr contained in a cerium-depleted mixed carbonate per year, which would represent less than 2% of the global primary market of approximately 60 million kilograms, according the ADAMAS Intelligence. At 2021 average prices, Medallion estimate the value of the contained NdPr produced each year by the proposed facility would be approximately $85 million – note that a mixed concentrate is worth less than the value of the contained REOs.
In April 2021, we announced completion of a suite of diagnostic test work at the Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organization (“ANSTO”) in Sydney, to extract REE from monazite. The monazite was sourced from an Australian mineral sand mine. Test work was focused on correlating low cost “diagnostic” mineralogical and chemical data from “run of mine” monazite with more comprehensive extraction results from the MMP.
Medallion commissioned Minviro Ltd. to complete a Life Cycle Assessment (“LCA”) to evaluate the environmental impact of processing byproduct monazite employing the MMP.
Monazite Feedstock
The Company has conducted a suite of diagnostic analysis at ANSTO evaluating the potential to process monazite from operating and prospective heavy mineral sand operations in Australia using the MMP process. As source material becomes available, we will continue to grow this data bank in order to help us optimize process conditions for a potential processing hub in Australia.
Medallion entered into a non-binding letter of intent (“LOI”) with Australian private company ACDC Metals Ltd (“ACDC”) to utilize Medallion’s proprietary MMP process. ACDC is securing three mineral sand properties and other exploration assets in Victoria, Australia. The LOI outlines various terms and conditions that will form the basis of a binding contract, subject to mutual due diligence, provides ACDC with the exclusive right to construct a mineral sand monazite refinery in southeastern Australia utilizing the MMP, and the right to sub-license the LAD Chromatography process for REE separation from us.
Medallion is in discussion with a range of partners regarding business opportunities in this area.
Ligand Assisted Development Process
In 2020 Medallion initiated a comparative technical review of existing and emerging REE separation technologies and, on February 18, 2021 announced the acquisition of an exclusive license to Purdue’s Ligand Assisted Displacement (“LAD”) chromatography process for the recovery of metals from raw material feedstocks excluding coal and recycled materials.
Medallion is supporting development of the LAD process through a three-year sponsored research program with Purdue, targeting the design, development, and operation of a demonstration plant. In June 2021 the Company announced successful separation and purification of Nd and Pr from an REE chemical concentrate derived from monazite processed via the MMP.
The LAD process is capable of processing complex multiple metal mixtures into individual metals (or groups) and, as such it may find uses in other separation processes which currently employ solvent extraction.
Medallion believes the LAD process will be a low-cost, environmentally friendly process that will be readily adaptable to different feedstocks, unlike current standard-practice in China and elsewhere.
Vertical Integration
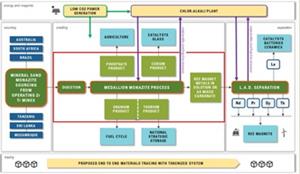
The MMP and LAD processes can operate independently or can be integrated into a combined facility processing monazite feedstock and producing separated rare earth oxides, as shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7: Conceptual REE monazite to magnet supply chain utilizing the Medallion Monazite Process and Purdue’s LAD Chromatography. Red box outlines the system boundary for the current Techno Economic Assessment
https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/5229cf5a-07bf-42d2-8170-061d331331be
About Medallion Resources
Medallion Resources (TSX-V: MDL; OTCQB: MLLOF; Frankfurt: MRDN) has developed a proprietary process and related business model to achieve low-cost, near-term, rare-earth element (REE) production by exploiting monazite. Monazite is a rare-earth phosphate mineral that is widely available as a by-product from mineral sand mining operations. Furthermore, Medallion has recently licensed from Purdue Research Foundation an innovative REE separation technology developed by Purdue University which can be utilized by Medallion and sub-licensed by Medallion to third party REE producers.
REEs are critical inputs to electric and hybrid vehicles, electronics, imaging systems, wind turbines and strategic defense systems. Medallion is committed to following best practices and accepted international standards in all aspects of mineral transportation, processing and the safe management of waste materials. Medallion utilizes Life Cycle Assessment methodology to support investment and process decision making.
More about Medallion (TSX-V: MDL; OTCQB: MLLOF; Frankfurt: MRDN) can be found at medallionresources.com.
Contact(s):
Mark Saxon, President & CEO
+1.604.681.9558 or msaxon@medallionresources.com
Neither TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in the policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this release.
Medallion management takes full responsibility for the content of and has prepared this news release. Some of the statements contained in this release are forward-looking statements, such as statements that describe Medallion’s plans with respect to general strategic matters and the advancement of its business plan, Medallion’s ability to advance and commercialize its technology platforms and negotiate commercial agreements with third parties, the potential completion of an up-listing to a U.S. exchange and related financing, and the completion of the licensing transaction with ACDC Metals Ltd.
Forward-looking statements are frequently, but not always, identified by words such as "expects," "anticipates," "believes," "intends," "estimates," "potential," "possible," "projects," "plans," and similar expressions, or statements that events, conditions or results "will," "may," "could," or "should" occur or be achieved or their negatives or other comparable words. Since forward-looking statements address future events and conditions, by their very nature, they involve inherent risks and uncertainties, including the risks related to market conditions and regulatory approval and other risks outlined in the Company’s management discussions and analysis of financial results. Actual results in each case could differ materially from those currently anticipated in these statements. These forward-looking statements are made as of the date of this press release, and, other than as required by applicable securities laws, Medallion disclaims any intent or obligation to update publicly any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or results or otherwise, except as required pursuant to applicable laws.
This news release shall not constitute an offer to sell or the solicitation of an offer to buy nor shall there be any sale of the securities in any jurisdiction in which such offer, solicitation or sale would be unlawful.