New Age Metals Completes Phase 3 Rhodium Geochemistry Study of the River Valley Palladium Project
(TheNewswire)
 | |||||||||
 |  |  |  | ||||||
-
Rhodium (Rh) (~US$ 7,950/ ounce, dated 9st May 2023) is the most valuable platinum group metal (PGM), with recent spot price highs of 5 times higher than Pd and 7 times higher than Pt
-
552 Rh new assay results for the Dana and Lismer Zones of the River Valley Palladium Deposit
-
Highest assay result is 0.306 g/t Rh, with 33 more samples returned assays ≥0.100 g/t Rh and a total of 113 samples returned assays 0.050 g/t Rh
-
The highest Rh concentrations generally coincide with the highest palladium (Pd) and platinum (Pt) grades
-
Rh concentrations in the River Valley Deposit are equivalent to approximately 9% of Pt grades
-
Based on encouraging results from Phases 1 to 3, subsequent phases of this multi-phase Rh evaluation program will take samples of PGE mineralized intervals from more of the mineralized zones for assay analysis and PGE mineralogical studies
-
The River Valley Deposit is one of North Americas largest undeveloped primary platinum-group metal projects with 2.3 Moz Pd+Pt+Au in the Measured + Indicated classifications and 1.6 Moz Pd+Pt+Au in the Inferred classification
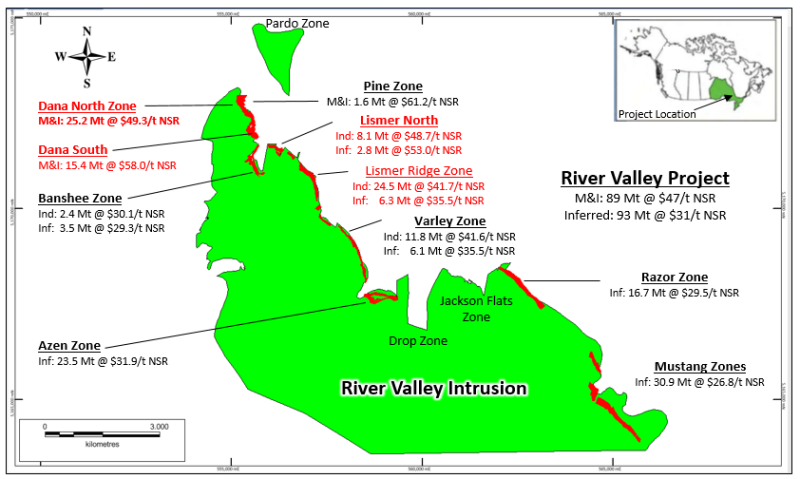
Rockport, Canada – TheNewswire - May 9, 2023 - New Age Metals Inc. (NAM) (TSXV:NAM); (OTC:NMTLF); (FSE:P7J) (“NAM” or the “Company”) announces completion of the Rh geochemistry study of the River Valley Palladium Deposit, 100 km east of Sudbury, Ontario. Phase 3 of the Rh geochemistry study collected 552 ¼ HQ core samples from four metallurgical drill holes completed in 2021 within the Dana North, Dana South, Lismer North and Lismer Ridge Zones. This announcement presents new Rh assay data for these 552 samples. These zones are located in the northern 5-km of the 16 km-long River Valley Palladium Deposit (Figure 1). In addition to Rh, the core samples were also assayed for gold (Au), iridium (Ir), palladium (Pd), platinum (Pt), and ruthenium (Ru) at the Geoscience Laboratories in Sudbury.
The new Rh data covered herein are in to addition to
data generated from recent and historical exploration drill core,
surface channel samples and grab samples of the River Valley
Deposit
(see NAM press releases dated
March 2, 2021 for Phase 1 and December 15, 2021 for the Phase 2
results; see also Pacific North West Capital Corp. press release dated
July 26, 2011). Rh is the most valuable platinum group
metal (PGM), with recent spot price highs of about US7950/oz Rh,
roughly 5 times higher than Pd and 7 times higher than Pt. However, Rh analyses are too costly to be performed on
every drill core assay sample. Rh is reported in the current Mineral
Resource Estimate for the River Valley Deposit (see NAM press release dated October 5,
2021), based on regression analysis of
historical drill core and channel sample assay data for the Dana and
Lismer Zones.
Figure 1. Distribution of 2021 updated pit constrained Mineral Resources at $15/t NSR cut-off at the River Valley Project. The mineralized zones labelled in red (Dana North, Dana South, Lismer North and Lismer Ridge) are the subject of this press release. Notes: M&I = Measured and Indicated Mineral Resources, Ind: = Indicated Mineral Resources, Inf = Inferred Mineral Resources.
The purpose of the multi-phase Rh geochemistry study program is three-fold:
-
1)Investigate Rh grades and distribution trends within the River Valley Deposit;
-
2)Develop a more robust regression technique to estimate Rh concentrations from Pt grades for future Mineral Resource Estimates; and
-
3)Investigate the potential of Rh as payable metal at River Valley.
Each of these topics are addressed below.
1) Rh Grade and Distribution Trends
In total, 552 samples of mineralized drill core
intervals in the four metallurgical holes were selected for Rh assay:
200 from Dana North, 148 from Dana South; 84 from Lismer North, and
120 from Lismer Ridge. Overall, the Rh assays values returned range
from 0.0007 g/t to 0.306 g/t Rh.
Thirty-four drill of the core samples returned assays of ≥0.100 g/t
Rh (Table 1) and 113 samples returned assays >0.050 g/t Rh. The
highest assay result for Ir is 0.069 g/t and for Ru is 0.039 g/t, also
for the samples from the Lismer Ridge Zone.
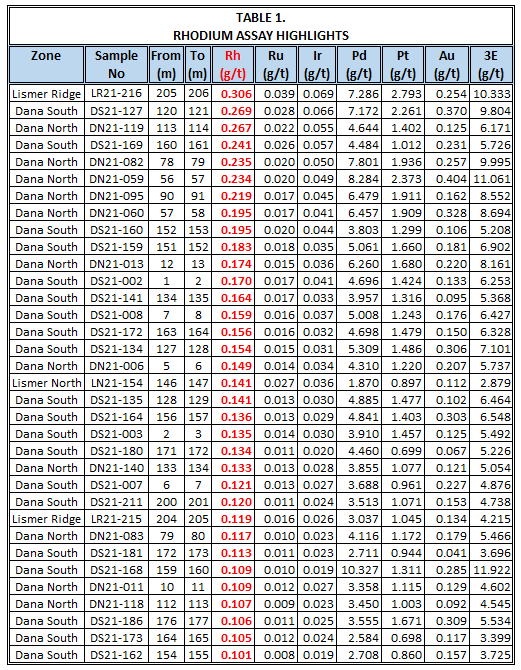
Note: *2.700 g/t Pd is the upper limit of detection for the analytical method employed by the assay lab, and therefore the higher Pd values listed can be regarded as provisional.
The announcement of these 552 results increases the total inventory of Rh data assays for River Valley to 8,610 (Table 2). At 80.2% of the total, the results for Dana North still dominate the inventory. However, the maximum Rh assay in this dataset is reported for the Lismer Ridge Zone, located 3 km south along strike from Dana North.
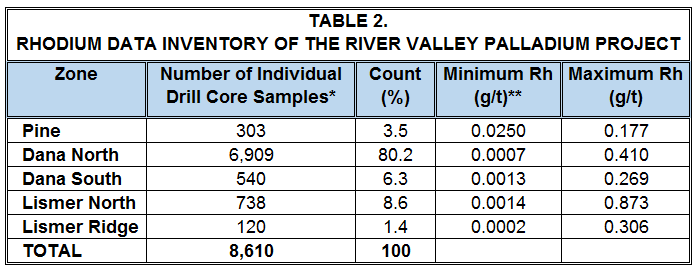
Notes: *drill core samples of mineralized intervals only
(channel samples, surface rock samples and academic study samples excluded)
**lower limit of detection = 0.000008 ppm Rh
Statistically, the assay results show strong positive
correlation of Rh with the other four PGE
(R2
>0.9) and moderate to strong correlation with Au (R2 >0.6) (Table
3), consistent with presence in the mineral phases Hollingworthite
[(Rh,Pt,Pd)AsS], platarsite [(PtAsS) with minor Rh and Ru), and
laurite [(RuS2 with minor
Rh], each of which has been identified in previous mineralogical and
scientific studies of River Valley. In contrast, Rh shows moderate
correlation (R2 >0.6) with Cu, Ni and S at the Dana Zones
and weak correlation (R2 <0.5) with Cu, Ni and particularly S at
the Lismer Zones. On the other hand, and as previously reported for
the Pine and Lismer North Zones, Rh (and Ru) do not correlate with
chromium (Rh R2 <0.010, and therefore is very unlikely to
be held in Cr-bearing phases like chromite. The evident occurrence of Rh independently
of chromite differs from other Rh-bearing PGE deposits elsewhere, and
could potentially benefit metallurgical recovery processes. Similarly,
the presence of laurite could bode well for potential Ru recovery.
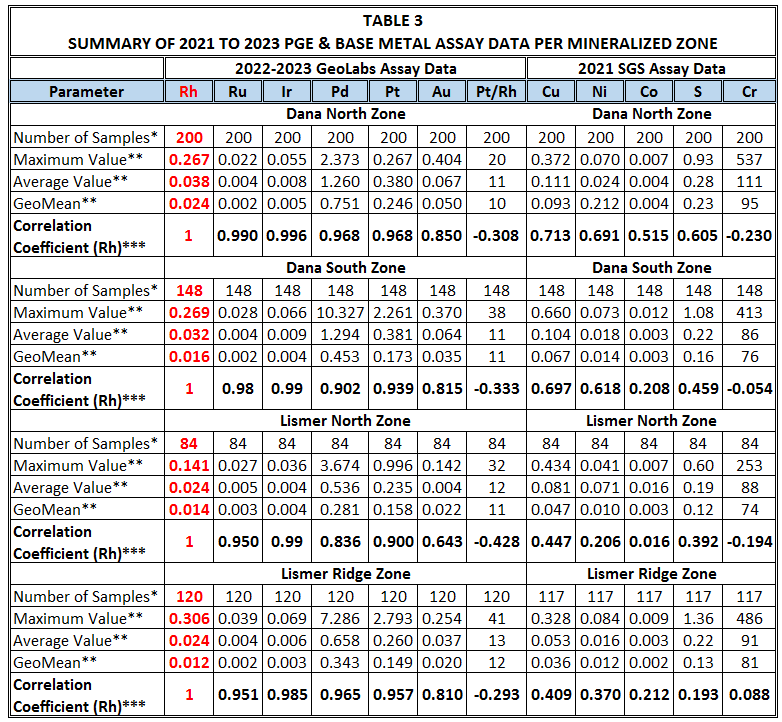
Notes: *2022-2023 assay data from Geoscience Laboratories and 2021 assay data from SGS Canada Inc. are for the same sampled drill core interval
**Au, Ir, Pd, Pt, Rh and Ru assay values in grams per tonne (g/t); Cu, Ni, and Co assay values in percent (%); Cr assay values in ppm
*** Correlation coefficient for rhodium
2) Development of a Reliable Regression Technique
Statistical analysis indicates that Rh assay values for the remaining River Valley Deposit (>100,000 samples) can be estimated on the basis of measured Pt values through regression analysis. A plot of measured Pt values versus Rh values for the 552 drill core samples assayed at Geoscience Labs and the non-linear regression line with its derived equation are shown in Figure 2. At this stage, non-linear regression models appear to be better than linear regression models for predicting higher Rh values.
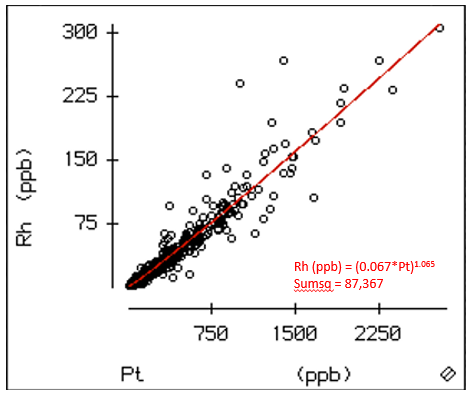
Figure 2. Plot of measured Pt versus Rh ppb values for the assayed mineralized drill core intervals (1044 samples) and the non-linear regression line with derived equation solved in DataDesk 8.2.1.
3) Investigate the Potential of Rh as Payable Metal at River Valley
In order to progress Rh studies further, subsequent phases of work will take samples of PGE mineralized intervals from additional mineralized zones to establish and confirm the spatial distribution of rhodium, where practical, throughout the River Valley Deposit. Specifically, the mineralized zones selected to be studied next include the Lismer Ridge Zone and the Varley Zone. Rhodium recovery testwork and detailed mineralogical investigations will be included in future metallurgical studies, in order to determine whether Rh could be a payable metal for a potential PGM mining operation at River Valley. Additionally, non-linear regression models will be further investigated for more even more reliable prediction of Rh contents, particularly higher values, where Rh assays are not available.
Rhodium
Rh is the rarest and most valuable of
the PGEs. The main use for Rh is in catalytic
converters designed to clean vehicle emissions. This metal is particularly effective in
cleaning nitric oxide emissions from internal combustion engine
vehicles. The majority of Rh is produced as a
by-product of platinum mining in South Africa. South Africa is the
world’s largest producer of Rh (~80%),
followed by Russia (~10%), Zimbabwe (~5%), Canada (~2%), and the USA
(~2%).
The global average mineral resource/reserve grade is 0.281 g/t Rh,
with the lowest reported mineral resource/reserve grade of 0.010 g/t
Rh and the highest reported mineral resource/reserve grade of 0.381
g/t Rh (source: S&P Global, 2020). As of May 1, 2023, the price of
rhodium is ~US$7,300/oz (source: Kitco May 1, 2023).
Assay Procedures & Quality Control
Drill (¼ HQ) core samples were selected by NAM geologists from PGE-Cu sulphide mineralized intervals in the Dana North and South and Lismer North and Ridge drill holes completed in 2021. The samples were delivered directly to Geoscience Laboratory in Sudbury for processing, preparation and assay analyses. Gold, iridium, palladium, platinum, rhodium and ruthenium were assayed by 30 g nickel fire assay with ICP-MS finish (IMP-200; ISO/IEC 17025 Accredited). Copper, nickel, cobalt, sulphur, Cr and 28 additional elements had previously been assayed by two-acid digestion and ICP-OES finish by SGS Laboratory in Burnaby, B.C. (see NAM press release dated March 1, 2022). Blanks and blind certified reference material (standards) samples were inserted at regular intervals for assay with the core samples, as part of NAM’s rigorous Quality Control program.
About the River Valley Palladium Project
The River Valley Palladium Project is located 100 road-km east from
the City of Sudbury.
The Project area is linked to Sudbury by a network of all-weather
highways, roads and rail beds and is accessible year-round with hydro
grid and natural gas power nearby. River Valley enjoys the strong
support of local communities, like the village of River Valley, 20 km
to the south.
A fully executed Memorandum of Understanding is in place with a local
First Nation. Environmental baseline studies re-commenced in 2020
are planned to continue through 2023.
The details of the 2021 updated Mineral Resource Estimate were announced in a Company press release dated October 5, 2021. At cut-offs of CDN$15/t NSR (pit constrained) and CDN$50/t NSR (out-of-pit), the Mineral Resource Estimate consists of: 89.9 Mt grading 0.54 g/t Pd, 0.21 g/t Pt, 0.04 g/t Au and 0.06% Cu, or CDN$47.58/t NSR in the Measured and Indicated classifications; and 94 Mt grading 0.35 g/t Pd, 0.16 g/t Pt, 0.04 g/t Au and 0.06% Cu, or CDN$31.69/t NSR in the Inferred classification. Contained metal contents are 2.3 Moz Pd+Pt+Au in the Measured and Indicated classifications and 1.6 Moz Pd+Pt+Au in the Inferred classification.
The 2019 Preliminary Economic Assessment (“PEA”) results for the River Valley Palladium Project were announced in a press release dated June 27, 2019, and are based on the 2019 updated Mineral Resource Estimate. The 2019 PEA outlines a 20,000 t/day open pit mine and processing plant operation producing an average of 119,000 ounces of PdEq per year over a mine life of 14 years. Using base case metal prices of US$1,200/oz Pd, $1,050/oz Pt and $3.25/lb Cu, the PEA showed a pre-tax NPV5% of US$261 million and a pre-tax IRR of 13%. At a +20% palladium price of $1,440/oz Pd, the pre-tax NPV5% increases to $501M and the pre-tax IRR to 19%.
The updated 2021 Mineral Resource Estimate forms a basis for the ongoing updated PEA of the River Valley Palladium Project. The updated PEA results are due to be released in the summer of 2023.
About NAM
New Age Metals is a junior mineral exploration and development company focused on the discovery, exploration and development of green metal projects in North America. The Company has two divisions; a Platinum Group Metals division and a Lithium/Rare Element division.
The PGM Division includes the 100% owned, multi-million-ounce,
district-scale River Valley Project, one of North America’s largest
undeveloped Platinum Group Metals Projects, situated
100 km by road east of Sudbury, Ontario. In addition to River Valley,
NAM owns 100% of the Genesis PGM-Cu-Ni Project in Alaska, and plans to
complete a surface mapping and sampling program in 2022.
The Company’s Lithium Division is one of the largest mineral claim holders in the Winnipeg River Pegmatite Field, where the Company is exploring for hard rock lithium and various rare elements such as tantalum, rubidium, and cesium. The company recently completed a phase two drill program at Lithium Two Project and is beginning to receive initial assay results. Further exploration plans for 2023/24 include continued mapping/sampling field programs following up on prospective trends outlined in the magnetic data and 2022 surface sampling, additional geophysical surveys, and diamond drilling. The company has a partnership with Mineral Resource Limited (MRL, ASX: MIN), a top global lithium producer to explore and develop the Company’s lithium project portfolio. The 2023/24 budget for our Manitoba Lithium Division has been submitted to MRL and a final budget is expected by mid-April 2023. The company is currently completing its 2022/23 $2.3 million budget.
Our philosophy is to be a project generator with the objective of optioning our projects with major and junior mining companies through to production. The Company is actively seeking an option/ joint venture partner for our newly acquired Northman, McLaughlin Lake, and South Bay Lithium Projects in Northern Manitoba, as well as its road-accessible Genesis PGM-Cu-Ni Project in Alaska.
Investors are invited to visit the New Age Metals website at www.newagemetals.com where they can review the company and its corporate activities. Any questions or comments can be directed to info@newagemetals.com or Harry Barr at Hbarr@newagemetals.com or Faraz Rasheed at Frasheed@newagemetals.com or call 613 659 2773.
If you have not done so already, we encourage you to sign up on our website (www.newagemetals.com) to receive our updated news.
The contents contained herein that relate to Exploration Results or Mineral Resources is based on information compiled, reviewed or prepared by Dr. Bill Stone, P.Geo., a consulting geoscientist for New Age Metals. Dr. Stone is the Qualified Person as defined by National Instrument 43-101 and has reviewed and approved the PGE/PGM-related technical content of this news release.
On behalf of the Board of Directors
“Harry Barr”
Harry G. Barr
Chairman and CEO
Neither the TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in the policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this release. Cautionary Note Regarding Forward Looking Statements: This release contains forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. These statements may differ materially from actual future events or results and are based on current expectations or beliefs. For this purpose, statements of historical fact may be deemed to be forward-looking statements. In addition, forward-looking statements include statements in which the Company uses words such as “continue”, “efforts”, “expect”, “believe”, “anticipate”, “confident”, “intend”, “strategy”, “plan”, “will”, “estimate”, “project”, “goal”, “target”, “prospects”, “optimistic” or similar expressions. These statements by their nature involve risks and uncertainties, and actual results may differ materially depending on a variety of important factors, including, among others, the Company’s ability and continuation of efforts to timely and completely make available adequate current public information, additional or different regulatory and legal requirements and restrictions that may be imposed, and other factors as may be discussed in the documents filed by the Company on SEDAR (www.sedar.com), including the most recent reports that identify important risk factors that could cause actual results to differ from those contained in the forward-looking statements. The Company does not undertake any obligation to review or confirm analysts’ expectations or estimates or to release publicly any revisions to any forward-looking statements to reflect events or circumstances after the date hereof or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events. Investors should not place undue reliance on forward-looking statements.
Copyright (c) 2023 TheNewswire - All rights reserved.